고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
- Disk Space Analyzer Windows
- Daisydisk For Pc
- Disk Usage Analyzer Daisydisk Windows Alternative Windows
Steps To Launch Disk Space Analyzer In Windows 10. Click on the start button and then head to the Settings. Now, click on “System.”. You can observe several options listed. You need to click on the “Storage” option. Finally, at the right-hand side of the window, you. If a license is not purchased there is a nag window (which suspends function) that pops up when loading the app (at user login). The nag pop-up is also summoned at certain time intervals and by performing a certain number of commands (manually or by keyboard shortcut).

| Developer(s) | Software Ambience |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2008 |
| Stable release | 4.10 (March 8, 2020; 41 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Operating system | macOS |
| Available in | English, German, French, Italian, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Japanese, Swedish, Spanish, Polish[2] |
| Type | Disk space analyzer |
| Website | daisydiskapp.com |
| Usage | |
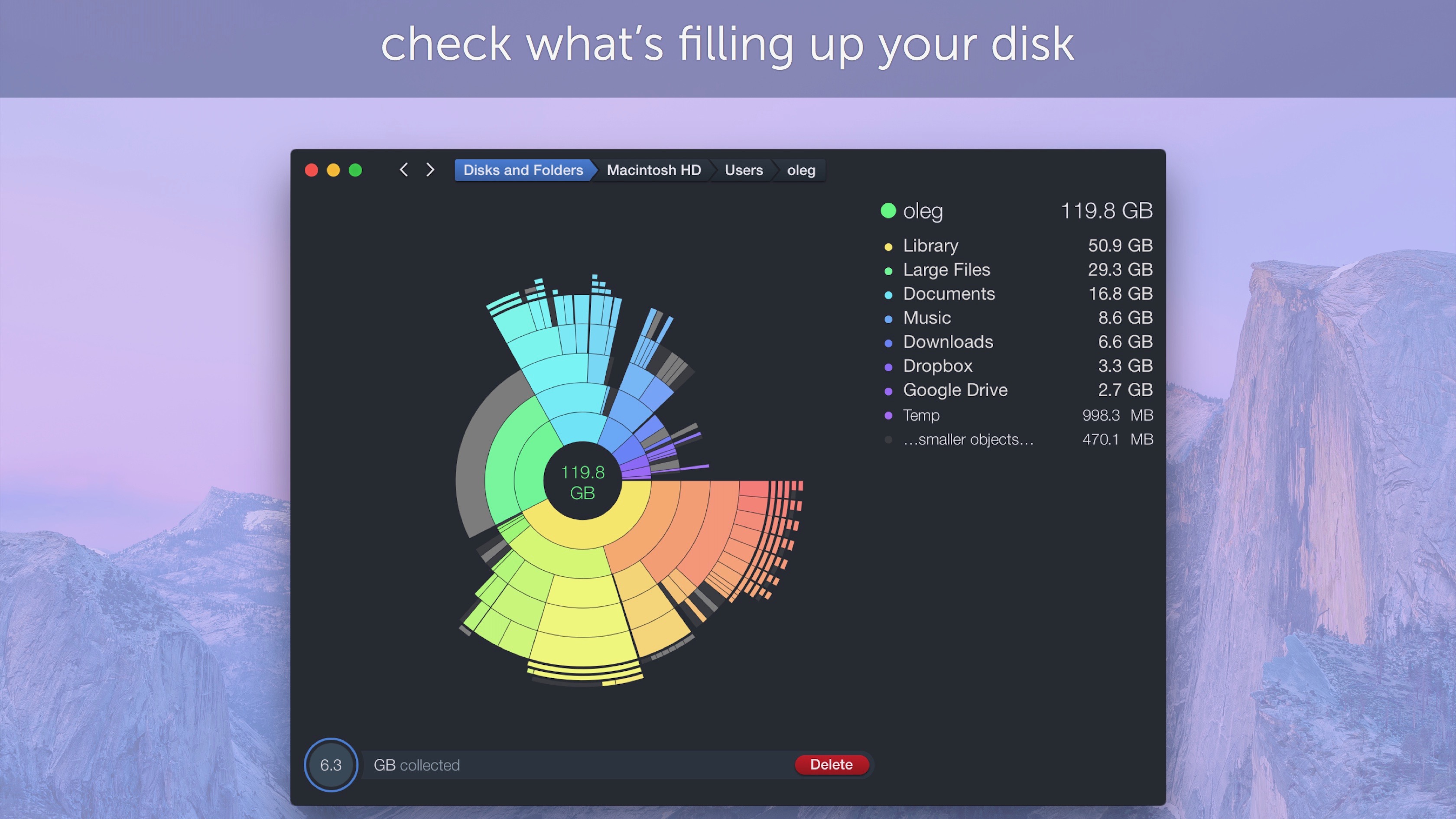
DaisyDisk is a paid disk space analyzer for macOS.[3] It displays a sunburst diagram of files on a hard drive to help with the location or deletion of large files.[4] It can display previews of files using Quick Look.[5][6][7] It also allows the user to look at the file directly in Finder, in order to delete it or move it elsewhere.[8]
History[edit]
DaisyDisk was started in late 2008 by interaction designer Taras Brizitsky and programmer Oleg Krupnov. They built the codebase from scratch to try to achieve higher speeds than similar programs. They decided to use a sunburst diagram as it is perceived better than other ways of visualizing data (such as treemaps).[9]
Features[edit]

DaisyDisk needs to scan the disk to create a map of its files and folders. Once the initial scan is completed, DaisyDisk keeps all displayed information up to date and reflects all changes to disk in real-time. DaisyDisk can scan multiple disks in parallel.
With v4.5[10] of DaisyDisk, support for APFS was added.[11]
Interface[edit]
DaisyDisk displays the contents as a color-coded sunburst diagram, resembling the petals of a daisy.[12] The interface places the root of the hard drive at the center of this daisy, and displays a hierarchical structure of that hard drive's file system that radiates from that center. This daisy is color-coded to differentiate between folders, while files themselves are always displayed as gray. In the right sidebar of the interface, DaisyDisk also provides a legend for these color codes. When hovering over a file or folder, the right sidebar of the interface updates with contextual information such as the file or folder name and their absolute path.[13] When clicking on a folder on the daisy, a new daisy is displayed with the chosen folder as its root. The interface shows a 'breadcrumb trail' of the current folder right above the sunburst diagram.[6]
DaisyDisk provides a Trash-like collector icon in the lower left of its interface where files and folders can dragged and dropped for deletion.[13]
As of DaisyDisk v3, a specialized version of the app exists for Mac users with Retina Displays.[14]
Integration[edit]
One of the ways DaisyDisk integrates with the Mac features is through its support of the Quick Look function, which is included in Mac OS X v10.5 'Leopard' and later. Hovering over any file or folder in DaisyDisk's interface and pressing space bar utilizes Quick Look and displays additional information about that file or folder in regards to its location and contents.[12]
References[edit]
- ^'DaisyDisk Release Notes'. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- ^'DaisyDisk Blog'. Software Ambience.
- ^'DaisyDisk 4.6.2 free download for Mac'. MacUpdate. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ^'DaisyDisk 4 Review'. Macworld. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ^'DaisyDisk: Tom's Mac Software Pick'. Lifewire. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ^ ab'DaisyDisk: Futuristic Data Visualization'. Mac.AppStorm. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^'How to identify the biggest space wasters on your Mac with DaisyDisk'. iDownloadBlog. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ^'Make Your HD Bigger with DaisyDisk for Mac [Review]'. Cult of Mac. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ^'An Evaluation of Space-Filling Information Visualizations for Depicting Hierarchical Structures'(PDF). Georgia Institute of Technology. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- ^'Top 5 questions about APFS and macOS High Sierra asked by Mac users'. DaisyDisk Blog. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^'How to free up disk space in macOS High Sierra'. Cult of Mac. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ ab'Review: DaisyDisk: Disk Visualization and Analyzer Tool for the Mac'. aboutTechnology. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
- ^ ab'Make Your HD Bigger with DaisyDisk for Mac [Review]'. Cult of Mac. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
- ^'DaisyDisk Blog'. Software Ambience. 7 September 2013. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
| Original author(s) | Fabio Marzocca |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Paolo Borelli |
| Stable release | 3.36.1[1] (2 April 2020; 16 days ago) [±] |
| Preview release | 3.35.91[2] (18 February 2020; 2 months ago) [±] |
| Repository | |
| Operating system | UNIX-like |
| Type | Disk utility |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Baobab |
| Usage | |
Disk Usage Analyzer is a graphical disk usage analyzer for GNOME. It was part of gnome-utils,[3] but was split off for GNOME 3.4. It was originally named Baobab after the Adansonia tree. The software gives the user a menu-driven, graphical representation of what is on a disk drive.[4] The interface allows for selection of specific parts of filesystem being scanned so a single folder, the entire filesystem, and even remote folders and filesystems can be scanned.[5] The graphical representation can be switched between a ring chart and a treemap chart so the presentation can be tailored to the specific content being scanned.[6]
In 2012[7][8], Disk Usage Analyzer was rewritten in Vala.[9]
Future[edit]
At the GNOME Users And Developers European Conference (GUADEC) in 2013, a plan to merge the Disk Usage Analyzer with gnome-system-monitor to a new program called Usage was presented.[10][11]
Similar programs[edit]
Disk Space Analyzer Windows
- For Windows: SpaceSniffer; WinDirStat (https://windirstat.net/)
- For Linux/Unix: KDirStat, which inspired WinDirStat; QDirStat,[12] and K4DirStat, based on KDirStat; GdMap; Filelight; ncdu
- For macOS: Disk Inventory X, inspired by WinDirStat;[13]GrandPerspective
References[edit]
- ^Catanzaro, Michael (2 April 2020). 'GNOME 3.36.1 Released'. GNOME Mail Services (Mailing list). Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^Catanzaro, Michael (18 Feb 2020). 'GNOME 3.35.91 released'. GNOME Mail Services (Mailing list). Retrieved 19 Feb 2020.
- ^GnomeUtils - GNOME Live!
- ^'Disk Usage Analyzer for GNOME'. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^'Baobab Usage'. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^'Baobab Shows'. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/baobab/commit/586355bd14c9a4b3b4f5f4563ebef66f84b8df93
- ^https://wiki.gnome.org/action/info/Apps/DiskUsageAnalyzer/ValaRewrite?action=info
- ^https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Baobab/ValaRewrite
- ^https://wiki.gnome.org/Design/Apps/Usage
- ^https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/SystemMonitor/MergeWithUsage SystemMonitor
- ^'Check Linux Disk Space from Terminal & Graphic Interface'. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- ^'Disk Inventory X'. Retrieved 1 Apr 2015.
The layout algorithm is based on KDirStat. The idea to develop this program came to me when a fellow of mine showed me his creation WinDirStat.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Disk Usage Analyzer. |





댓글 영역